OneHundredCoffee is reader-supported, and some products displayed may earn us an affiliate commission. Details
Understanding The Potential Benefits Of Coffee With Metformin
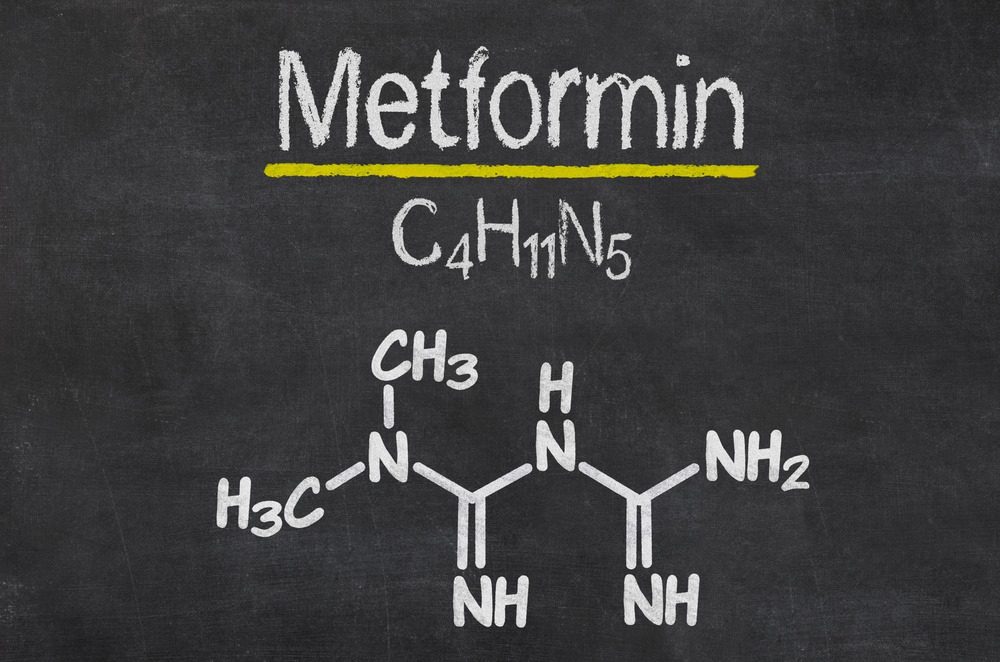
Metformin is the quiet workhorse of type 2 diabetes care—steady, dependable, and rarely dramatic. Coffee, on the other hand, is a daily ritual with personality: the smell that wakes you up, the sip that signals “go.” Bringing them together is less about rules and more about rhythm. The goal isn’t to force your morning into a medical checklist; it’s to let metformin do its job while your coffee remains something you actually look forward to.
Start with what metformin is trying to do. It smooths out the liver’s overnight glucose output, helps your muscles use sugar more effectively, and—when taken consistently—nudges A1C in the right direction. Coffee brings caffeine, organic acids, and flavorful polyphenols that can feel different for each person. Some people notice sharper focus and easier workouts; others feel a little jittery, a touch of reflux, or a later bedtime. None of that means coffee is “off-limits.” It means you can make small, smart adjustments that respect both your medication and your ritual.
Timing is the easiest lever. If metformin upsets your stomach, take it with a meal and enjoy coffee afterward rather than on an empty stomach. If caffeine makes your blood sugar a bit bouncy, try a smaller cup, a gentler roast, or switch to half-caff/decaf on days you want ultra-steady energy. If sleep is precious (and metabolic health loves sleep), keep your last cup to early afternoon and sip water as a default beverage later in the day.
Your brew method matters, too. Paper-filtered drip or pour-over tends to be friendlier on the stomach than unfiltered methods. Cold brew diluted with water or milk can feel smoother. And bean choice is a quiet superpower: low-acid decaf or balanced medium roasts can deliver the comfort of coffee with fewer “edges.” Think of them as tools, not compromises.
Most importantly, personalize. Keep an eye on patterns—does coffee before breakfast feel different than coffee with breakfast? Do large, fast cups bother you more than smaller, slower ones? Metformin is long-game medicine; your coffee can be, too. With a few gentle tweaks, you can keep the cup you love while letting your medication work in the background—no drama, just a routine that fits your life.
Coffee × Metformin — Quick Guide & Safest Beans Pick
| Medicine | Coffee effect snapshot | Practical guidance | Simple timing tip | Safest beans pick* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metformin | Coffee may add alertness but can nudge reflux/jitters or sleep in sensitive users. | Favor paper-filtered brews; choose low-acid decaf/half-caff on days you want ultra-steady energy. | Take metformin with a meal; enjoy coffee with/after food or ~60–90 min apart if you’re sensitive. | Verena Street “Sunday Drive” Decaf — Ground, 11 oz (Swiss Water) |
*“Safest beans” = typically low-acid, decaf, or half-caff options that many people on metformin find gentler on stomach, sleep, and day-to-day glucose steadiness. Adjust to your own tolerance and clinician advice.
In conclusion, the combination of coffee with metformin holds potential benefits for individuals with type 2 diabetes. Coffee’s bioactive compounds may enhance glucose metabolism, while its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties could contribute to better management of diabetes-related complications. Nevertheless, further research is needed to elucidate the exact mechanisms underlying these potential synergistic effects and establish specific recommendations regarding coffee consumption alongside metformin therapy.
Exploring The Role Of Metformin In Weight Loss
Metformin, a widely prescribed drug for managing type 2 diabetes, has been garnering attention for its potential role in weight loss. While primarily used to regulate blood sugar levels, this medication has shown promising effects on body weight and metabolism. As researchers delve deeper into understanding metformin’s mechanisms of action, its potential as an adjunct therapy for weight loss becomes increasingly intriguing.
One key way metformin aids in weight loss is by reducing appetite and food intake. Studies have revealed that this medication can suppress hunger signals from the brain, leading to a decreased desire to eat. By modulating appetite-regulating hormones such as ghrelin and leptin, metformin helps individuals feel more satisfied with smaller portions. This effect is especially beneficial for those struggling with overeating or emotional eating patterns.
Additionally, metformin has been found to improve insulin sensitivity and reduce insulin resistance – two factors strongly associated with obesity. Insulin resistance occurs when cells become less responsive to the hormone insulin, leading to elevated blood sugar levels and increased fat storage. By enhancing insulin sensitivity, metformin helps the body utilize glucose more efficiently and prevents excess fat accumulation.
Furthermore, metformin may have a direct impact on fat metabolism by promoting the breakdown of stored fats (lipolysis) and inhibiting their synthesis (lipogenesis). This dual action facilitates the mobilization of fatty acids from adipose tissue while preventing new fat formation. Consequently, individuals taking metformin may experience a reduction in body fat percentage and overall weight.
Interestingly, recent research suggests that metformin may also influence gut microbiota composition – the vast community of microorganisms residing within our digestive system. Mounting evidence indicates that certain types of gut bacteria play a crucial role in energy regulation and weight management. Metformin appears to alter these bacterial populations favorably by increasing beneficial bacteria while decreasing harmful ones. This microbial shift may contribute to improved metabolic health and weight loss.
While metformin shows promise as a weight-loss aid, it is essential to recognize that individual responses vary. Factors such as genetics, lifestyle choices, and underlying medical conditions can influence its effectiveness. Metformin’s impact on weight loss is typically modest, with studies reporting an average reduction of 1-2 kilograms over several months. Therefore, it is crucial to view metformin as part of a comprehensive approach to weight management that includes dietary modifications, regular exercise, and behavioral changes.
In conclusion, metformin’s potential role in weight loss extends beyond its primary use in diabetes management. By suppressing appetite, improving insulin sensitivity, modulating fat metabolism, and influencing gut microbiota composition, this medication offers various mechanisms through which it may facilitate weight loss. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before considering metformin solely for this purpose. Understanding individual factors and incorporating other lifestyle changes are crucial components of achieving sustainable and successful weight management goals.
The Synergistic Effects Of Caffeine And Metformin On Weight Management
Weight management is a complex process that often requires a combination of lifestyle modifications and pharmacological interventions. Among the various strategies available, the combination of caffeine and metformin has gained attention due to its potential synergistic effects on weight loss. Both caffeine and metformin have been individually studied for their effects on metabolism and body weight, but recent research suggests that their combined use may offer additional benefits in promoting weight management.
Caffeine, commonly found in coffee and tea, is a widely consumed psychoactive substance known for its stimulant properties. It acts by increasing energy expenditure, promoting lipolysis (breakdown of fat), and suppressing appetite. These effects can potentially contribute to weight loss efforts. On the other hand, metformin is an oral medication primarily used to treat type 2 diabetes but has also been investigated for its impact on body weight regulation.
Metformin works by improving insulin sensitivity, reducing hepatic glucose production, and enhancing glucose uptake in peripheral tissues.
When caffeine and metformin are combined, several mechanisms may contribute to their synergistic effects on weight management. Firstly, both substances have been shown to increase energy expenditure through thermogenesis – the production of heat by the body as a result of metabolic processes. This increased energy expenditure can help create a calorie deficit necessary for weight loss.
Moreover, studies have suggested that caffeine enhances the effectiveness of metformin in improving insulin sensitivity. By reducing insulin resistance – a key factor in obesity – this combination could lead to better glycemic control and reduced fat accumulation. Additionally, caffeine intake has been associated with increased fatty acid oxidation during exercise when combined with metformin therapy compared to either treatment alone.
Furthermore, the appetite-suppressing properties of both substances may work together to promote satiety and reduce overall caloric intake throughout the day. Caffeine stimulates the central nervous system while metformin affects gut hormones involved in appetite regulation. Together, they may create a stronger satiety signal that helps individuals adhere to a reduced-calorie diet.
While the combination of caffeine and metformin shows promise for weight management, it is important to note that individual responses may vary. Factors such as genetics, lifestyle habits, and underlying health conditions can influence the effectiveness of this combination therapy. Additionally, potential side effects and drug interactions should be considered when combining these substances.
In conclusion, the synergistic effects of caffeine and metformin on weight management offer a promising avenue for those seeking effective strategies to combat obesity. By enhancing energy expenditure, improving insulin sensitivity, and suppressing appetite, this combination may provide additional benefits compared to either substance alone. However, further research is needed to fully understand the optimal dosage and long-term effects of this combination therapy.
How Coffee Consumption Can Enhance The Effects Of Metformin
In recent years, researchers have discovered that coffee may have additional health benefits beyond its energizing properties. Interestingly, studies suggest that coffee consumption can enhance the effects of metformin, a commonly prescribed medication for type 2 diabetes management. Let’s delve into how coffee interacts with metformin and why this combination might be advantageous for individuals with diabetes.
Metformin is an oral antidiabetic drug that works by reducing glucose production in the liver and improving insulin sensitivity in muscle cells. It is widely prescribed due to its effectiveness in managing blood sugar levels and its relatively low risk of adverse side effects. However, some individuals with diabetes may experience limited response or resistance to metformin over time. This is where the potential synergy between coffee and metformin comes into play.
Numerous studies have indicated that coffee consumption can increase insulin sensitivity and improve glucose metabolism – mechanisms similar to those targeted by metformin. For instance, a study published in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism found that habitual coffee consumption was associated with lower insulin resistance in individuals at risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Another study published in Diabetes Care showed that consuming caffeinated coffee improved postprandial glycemic control compared to decaffeinated coffee or water.
The key bioactive components responsible for these beneficial effects are caffeine and chlorogenic acids found abundantly in coffee beans. Caffeine has been shown to enhance insulin sensitivity by activating adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) – a cellular energy sensor involved in glucose regulation. Chlorogenic acids, on the other hand, possess antioxidant properties and can help reduce inflammation associated with impaired glucose metabolism.
When combined with metformin, these compounds present in coffee may potentiate its therapeutic effects. Metformin primarily works by activating AMPK, similar to caffeine, resulting in decreased glucose production and increased glucose uptake in muscle cells. Therefore, the co-administration of coffee and metformin may have an additive or synergistic effect on improving insulin sensitivity and glycemic control.
It is worth noting that individual responses to coffee and metformin may vary depending on factors such as genetics, overall health status, and lifestyle choices. Additionally, excessive coffee consumption can lead to side effects like jitteriness, insomnia, or gastrointestinal discomfort. Therefore, moderation is key when considering the combination of coffee with metformin.
In conclusion, emerging evidence suggests that coffee consumption can enhance the effects of metformin in managing blood sugar levels for individuals with type 2 diabetes. The shared mechanisms of action between coffee compounds and metformin highlight their potential synergy in improving insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism. Nonetheless, individuals need to consult with their healthcare provider before making any significant changes to their medication regimen or dietary habits.
Investigating The Impact Of Caffeine On Blood Sugar Control With Metformin
Metformin is a commonly prescribed medication for the management of type 2 diabetes. It works by reducing glucose production in the liver and improving insulin sensitivity in the body. As millions of people rely on metformin to control their blood sugar levels, it is essential to understand how other substances, such as caffeine, may interact with this medication.
Caffeine, found in various beverages like coffee, tea, and energy drinks, has stimulant properties that can affect our central nervous system. It is known to increase alertness and temporarily boost metabolism. However, its impact on blood sugar levels remains a topic of interest among researchers.
Several studies have investigated the potential interaction between caffeine and metformin in blood sugar control. Understanding this relationship can help individuals make informed decisions about their dietary habits while taking metformin.
One study conducted by researchers from the University of Guelph explored how caffeine affects blood glucose levels when combined with metformin. The study involved individuals diagnosed with type 2 diabetes who were already taking metformin as part of their treatment regimen. Participants were given either a caffeinated or a decaffeinated beverage before undergoing an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT).
The results showed that consuming a caffeinated beverage before an OGTT led to higher blood glucose levels compared to those who consumed decaffeinated beverages before testing. This suggests that caffeine may interfere with the effectiveness of metformin in controlling blood sugar levels.
Another study published in Diabetes Care investigated whether coffee intake had any effect on glycemic control among individuals with type 2 diabetes taking metformin as their primary treatment. The research included over 1,000 participants and monitored their coffee consumption habits over the years.
The findings indicated that increased coffee consumption was associated with worsened glycemic control among those using metformin therapy alone. Individuals who consumed higher amounts of coffee experienced higher fasting blood glucose levels and HbA1c values, indicating poorer blood sugar control.
However, it is essential to note that these studies provide observational evidence rather than definitive cause-and-effect relationships. While the results suggest a potential interaction between caffeine and metformin, further research is needed to establish a clearer understanding of this relationship.
Nevertheless, for individuals with type 2 diabetes taking metformin, it may be prudent to moderate caffeine intake as a precautionary measure. It is advisable to consult with healthcare professionals about personal dietary choices and any potential interactions between caffeine and metformin.
In conclusion, investigating the impact of caffeine on blood sugar control with metformin has yielded interesting findings. While research suggests that caffeine consumption may interfere with the effectiveness of metformin in controlling blood sugar levels, more studies are required to establish conclusive evidence. As always, individuals should consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice regarding their dietary choices while taking metformin.
Does Adding Coffee To Your Metformin Routine Promote Sustained Weight Loss?
Metformin, a medication commonly prescribed for the treatment of type 2 diabetes, has gained attention in recent years for its potential role in weight management. Alongside its blood sugar-regulating properties, metformin has been linked to modest weight loss in individuals with obesity or overweight. As coffee is one of the most consumed beverages worldwide, it is natural to wonder whether adding coffee to your metformin routine could enhance and sustain weight loss efforts.
Coffee, when consumed without additives like cream or sugar, is a low-calorie beverage that contains various bioactive compounds. Caffeine, one of the key components of coffee, has been shown to increase thermogenesis (the production of heat by the body) and fat oxidation (the breakdown of stored fat). These effects can potentially contribute to weight loss.
Several studies have examined the combined effects of metformin and coffee on body weight. A study published in Diabetes Care found that individuals who consumed both metformin and caffeine had greater reductions in body mass index (BMI) compared to those who only took metformin. Another study published in Obesity Research & Clinical Practice reported that drinking caffeinated coffee was associated with greater long-term weight loss success among individuals taking metformin.
The potential mechanisms behind this association are still being explored, but may be related to caffeine’s ability to suppress appetite and increase energy expenditure. Caffeine stimulates the central nervous system and enhances alertness while reducing feelings of hunger. This can lead to decreased calorie intake throughout the day.
However, it is important to note that excessive consumption of caffeine can have adverse effects such as increased heart rate, jitteriness, or disrupted sleep patterns. Therefore, moderation is key when incorporating coffee into your daily routine alongside metformin.
Furthermore, it is essential to consider the individual’s overall dietary habits and lifestyle choices. While coffee may provide some benefits, sustained weight loss requires a comprehensive approach that includes a balanced diet and regular physical activity. Coffee alone cannot replace healthy eating habits and an active lifestyle.
Additionally, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before making any changes to your medication or caffeine intake. They can provide personalized advice based on your specific health needs and potential drug interactions.
In conclusion, adding coffee to your metformin routine may have some potential benefits for promoting sustained weight loss. The caffeine in coffee can increase thermogenesis and fat oxidation while suppressing appetite, potentially aiding in weight management efforts. However, moderation is key when consuming caffeinated beverages, as excessive intake can have adverse effects. It is important to remember that coffee alone cannot substitute for a healthy lifestyle encompassing a balanced diet and regular exercise.
Maximizing The Benefits: Optimal Timing And Dosage For Combining Coffee And Metformin
Combining coffee with Metformin, a commonly prescribed medication for type 2 diabetes, has gained attention due to its potential health benefits. Both coffee and Metformin have been individually linked to improved glucose metabolism and reduced risk of certain diseases. However, to maximize the benefits of this combination, it is essential to consider the optimal timing and dosage for consumption.
Timing plays a crucial role in achieving the desired effects of combining coffee and Metformin. Research suggests that consuming coffee before or during a meal can help regulate postprandial glucose levels effectively. The caffeine present in coffee stimulates the release of insulin, which aids in the uptake of glucose by cells. By consuming coffee alongside a meal that includes carbohydrates, blood sugar spikes can be prevented or minimized.
It is important to note that individual responses may vary due to factors such as metabolism and sensitivity to caffeine. Therefore, finding the optimal timing for combining coffee with Metformin should be based on personal experience under medical supervision.
In addition to timing, understanding the appropriate dosage is crucial for achieving maximum benefits while minimizing potential risks associated with combining these substances. When considering dosage adjustments, it is important not only to factor in the amount of coffee consumed but also other sources of caffeine intake throughout the day.
Metformin doses are typically prescribed by healthcare professionals based on individual needs and responses to treatment. It is advisable not to exceed these recommended doses when incorporating coffee into one’s routine. Higher doses of caffeine may lead to adverse effects such as increased heart rate, jitteriness, or sleep disturbances in some individuals.
To optimize benefits while avoiding potential side effects from excessive caffeine consumption, moderation is key. Gradually introducing small amounts of coffee into your routine alongside Metformin allows for careful monitoring of its effects on blood sugar levels without overwhelming your system.
Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels becomes especially important when combining coffee and Metformin. By keeping track of your glucose readings before and after consuming coffee, you can determine the impact on your blood sugar levels more accurately. This data can assist in adjusting the timing, dosage, or even considering alternative options if necessary.
Lastly, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating coffee into your routine alongside Metformin. They can provide personalized guidance based on your specific health needs and any potential interactions with other medications you may be taking.
In conclusion, maximizing the benefits of combining coffee with Metformin involves careful consideration of both timing and dosage. Consuming coffee before or during a meal can help regulate postprandial glucose levels effectively. Finding the optimal timing should be based on personal experience under medical supervision. Moderation is essential to avoid excessive caffeine intake while gradually introducing small amounts of coffee into one’s routine alongside Metformin.
Considering Potential Side Effects And Risks Of Coffee With Metformin
Metformin is a widely prescribed medication for the management of type 2 diabetes. It helps to control blood sugar levels by improving insulin sensitivity and reducing glucose production in the liver. While it is generally safe and well-tolerated, combining metformin with coffee may have potential side effects and risks that individuals should be aware of.
One of the primary concerns when consuming coffee with metformin is its impact on gastrointestinal symptoms. Both coffee and metformin are known to cause gastrointestinal disturbances such as nausea, diarrhea, and stomach upset. When combined, these effects may be intensified, leading to more pronounced discomfort. It is important for individuals taking metformin to monitor their tolerance for coffee and adjust their intake accordingly.
Caffeine, the main active compound in coffee, has stimulant properties that can affect heart rate and blood pressure. Metformin itself does not typically cause significant changes in cardiovascular function; however, combining it with coffee may increase the risk of developing irregular heart rhythms or palpitations. Individuals with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions should exercise caution when consuming coffee along with metformin.
Furthermore, both coffee and metformin have diuretic effects on the body. This means they promote increased urine production, potentially leading to dehydration if water intake is not sufficient. Dehydration can have adverse effects on overall health and exacerbate certain conditions, such as kidney problems or electrolyte imbalances. Individuals taking metformin should ensure they stay adequately hydrated when consuming coffee to minimize this risk.
Another consideration when combining coffee with metformin is its potential impact on blood sugar control. While both substances have been shown to independently improve glucose metabolism, their combined effect may result in unpredictable fluctuations in blood sugar levels. Coffee has been found to temporarily increase blood sugar levels in some individuals due to its caffeine content stimulating certain hormones involved in glucose regulation.
Therefore, regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is crucial when consuming coffee with metformin to ensure optimal glycemic control.
Lastly, it is worth mentioning that coffee can interfere with the absorption of certain medications, including metformin. Some compounds present in coffee, such as polyphenols, may bind to medication molecules and reduce their bioavailability. To minimize this potential interaction, it is recommended to take metformin at least one hour before or two hours after consuming coffee.
In conclusion, while enjoying a cup of coffee may be a daily ritual for many individuals, those taking metformin should consider the potential side effects and risks associated with this combination. Gastrointestinal symptoms, cardiovascular effects, diuretic properties leading to dehydration, unpredictable blood sugar fluctuations, and potential interference with medication absorption are all factors that should be taken into account. Individuals on metformin therapy should consult with their healthcare provider regarding their specific circumstances and make informed decisions about incorporating coffee into their routine while closely monitoring any adverse reactions.
Tips For Incorporating Coffee Into Your Metformin Regimen Safely And Effectively
If you are a coffee lover who also takes metformin to manage your diabetes, you may be wondering how to safely incorporate coffee into your daily routine without compromising the effectiveness of your medication. While consuming coffee can have certain implications for those taking metformin, with a few considerations and adjustments, you can enjoy your cup of joe while managing your condition effectively.
Here are some tips to help you incorporate coffee into your metformin regimen safely:
1. Timing is key: To minimize any potential interactions between coffee and metformin, it is advisable to consume them separately. Coffee contains compounds that may interfere with the absorption of metformin, reducing its efficacy. Therefore, it is recommended to wait at least one hour after taking your medication before enjoying a cup of coffee.
2. Monitor blood sugar levels: Coffee can affect blood sugar levels in some individuals, potentially leading to fluctuations that may impact the effectiveness of metformin. Regularly monitoring your blood sugar levels will help you identify any patterns or changes associated with caffeine consumption and adjust your treatment plan accordingly.
3. Consider decaffeinated options: If you find that caffeine affects your blood sugar levels or if you prefer to limit caffeine intake, opting for decaffeinated coffee can be a suitable alternative. Decaffeinated varieties still offer the rich taste and aroma of regular coffee without the potential side effects associated with caffeine.
4. Watch for adverse reactions: Some individuals may experience gastrointestinal side effects when combining metformin with caffeinated beverages like coffee due to their stimulant properties. Pay attention to any adverse reactions such as nausea or stomach discomfort and consult with your healthcare provider if needed.
5. Balance fluid intake: Both metformin and caffeine have diuretic properties, which can increase urination frequency and potentially lead to dehydration if not managed properly. Ensure that you drink enough water throughout the day to stay properly hydrated and counterbalance the diuretic effects.
6. Mind the additives: When enjoying your coffee, be mindful of the additives you use. Creamers, sweeteners, and flavored syrups can contain added sugars or artificial sweeteners that may impact blood sugar levels. Opt for natural sweeteners like stevia or cinnamon instead.
7. Seek professional advice: As everyone’s medical condition is unique, it is crucial to consult with your healthcare provider or diabetes educator before making any significant changes to your coffee consumption habits while taking metformin. They can offer personalized guidance tailored to your specific needs and help you navigate any potential concerns effectively.
Remember, while incorporating coffee into your metformin regimen is possible, it is essential to monitor your body’s response and make adjustments accordingly. By following these tips and working closely with your healthcare team, you can enjoy a cup of coffee without compromising the effectiveness of your medication or jeopardizing your diabetes management efforts.
Conclusion: Harnessing The Power Of Coffee With Metformin For Enhanced Weight Loss Results
The combination of coffee and metformin has shown promising potential in enhancing weight loss results. This powerful duo offers a multifaceted approach to tackling obesity and metabolic disorders, providing individuals with an effective tool to reach their weight loss goals. By understanding the mechanisms behind this synergy and implementing it as part of a comprehensive weight management plan, individuals can experience improved outcomes in their journey towards a healthier lifestyle.
Metformin’s ability to regulate blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity has long been recognized in the field of diabetes management. However, recent studies have shed light on its additional benefits for weight loss. By targeting key pathways involved in metabolism, metformin can help reduce appetite, increase fat oxidation, and promote calorie expenditure. These effects are particularly beneficial for individuals struggling with obesity or metabolic syndrome.
When combined with coffee consumption, these effects are further potentiated. Coffee contains caffeine, a natural stimulant that has been shown to boost metabolism and increase energy expenditure. Additionally, coffee is rich in antioxidants that have been linked to various health benefits, including reducing inflammation and improving insulin sensitivity.
Furthermore, emerging evidence suggests that caffeine may enhance the action of metformin by improving its bioavailability and extending its half-life in the body. This synergistic effect could potentially lead to enhanced weight loss outcomes compared to using either substance alone.
Incorporating coffee with metformin into a weight loss regimen requires careful consideration of individual factors such as caffeine sensitivity and existing medical conditions. Individuals must consult with their healthcare providers before embarking on this approach to ensure safety and efficacy.
Additionally, it is important to note that while coffee with metformin may offer significant benefits for weight loss efforts, it should not be considered a miracle solution or a replacement for healthy lifestyle habits. A balanced diet rich in whole foods along with regular physical activity remains the cornerstone of any successful weight management plan.
Future research should focus on elucidating the optimal dosage and timing of coffee with metformin for weight loss purposes. Furthermore, long-term studies are needed to assess the sustainability and potential side effects of this combination therapy.
Coffee with Metformin: When to Sip, What to Avoid, and Why It Matters — FAQ
Covers immediate-release (IR) and extended-release (XR) metformin. Educational only—follow your clinician’s advice for your plan.
1) Can I drink coffee while taking metformin?
Yes. Coffee doesn’t block metformin’s glucose-lowering effect. Focus on consistency, hydration, and taking metformin as directed.
2) Best timing: before, with, or after coffee?
Metformin is usually taken with meals to lower GI upset. If coffee is part of your meal, that’s fine. For sensitive stomachs, sip coffee after eating or choose smaller, gentler cups.
3) Will coffee raise or lower my blood sugar on metformin?
Caffeine can nudge glucose and insulin responses in some people. Metformin blunts liver glucose output, but you may still see small CGM/meter shifts. Track your own pattern.
4) Does coffee worsen metformin’s GI side effects?
It can for some. If you get nausea, reflux, or loose stools, reduce caffeine, avoid very hot or very large cups, switch to XR, and always take with food unless told otherwise.
5) IR vs XR—any coffee differences?
XR is gentler on the gut for many people, so coffee tolerance may improve. Still take with a meal. Don’t split or crush XR tablets.
6) How much caffeine per day is reasonable?
Many adults do well at 100–200 mg/day while optimizing glucose and sleep. Higher intakes can worsen jitters, reflux, and sleep—indirectly affecting glucose control.
7) Is decaf better for glucose control?
Often yes for caffeine-sensitive people. Decaf keeps flavor with minimal caffeine, which may stabilize readings and reduce GI or sleep issues.
8) What should I avoid adding to coffee on metformin?
Limit large sugar syrups and heavy sweeteners that spike glucose. Full-fat creamers are fine in small amounts, but watch calories if weight loss is a goal.
9) Bulletproof coffee and fasting—good idea?
High-fat coffee breaks a strict fast and adds significant calories. If your plan includes time-restricted eating with metformin, choose plain coffee or minimal additions unless your clinician advises otherwise.
10) Morning spikes after coffee—normal on metformin?
Dawn phenomenon plus caffeine can lift glucose for some. Try smaller cups, decaf, adding protein/fiber to breakfast, or shifting coffee later.
11) Does coffee increase the risk of lactic acidosis?
Lactic acidosis with metformin is rare and tied to major risk factors (severe kidney/liver failure, severe dehydration, hypoxia). Coffee itself isn’t a known trigger—avoid dehydration and follow hold rules during acute illness.
12) Sick day rules—what about coffee?
If vomiting, dehydrated, or not eating, many plans advise pausing metformin until eating and drinking normally. Choose water or oral rehydration first; skip coffee if it worsens symptoms.
13) Lab days and procedures—can I have coffee?
Follow fasting instructions exactly. For iodinated contrast procedures, you may be told to hold metformin temporarily; coffee rules depend on the facility’s fasting policy.
14) Does milk in coffee affect metformin or glucose?
Milk adds carbs and calories. Small amounts usually have minor impact; track your readings. If lactose-sensitive, choose lactose-free or alternatives.
15) Will coffee cause hypoglycemia with metformin?
Metformin alone rarely causes low glucose. Risk rises if combined with insulin or sulfonylureas. If you take those, carry quick carbs and monitor closely around caffeine and exercise.
16) Best time of day for coffee on metformin?
Morning or early afternoon works for most. Avoid late caffeine that disturbs sleep; poor sleep can worsen insulin resistance and appetite the next day.
17) Can coffee change how much weight I lose on metformin?
Plain coffee is low-calorie and may slightly curb appetite; sugary drinks can add calories and stall progress. Track intake and choose additions wisely.
18) Exercise, coffee, and metformin—any tips?
Light caffeine pre-workout may boost energy. Stay hydrated, avoid large doses if prone to tachycardia, and watch glucose if you use insulin or sulfonylureas.
19) B12 and metformin—does coffee matter?
Metformin can lower B12 over time in some people; coffee doesn’t change that risk. Ask your clinician about periodic B12 checks if you’ve been on long-term therapy.
20) Quick rules of thumb to keep it simple
- Take metformin with meals; pair coffee with food if you’re sensitive.
- Keep caffeine modest and consistent; use decaf if jittery or refluxy.
- Limit sugar-heavy add-ins; watch total calories.
- Hydrate well, especially on exercise or hot days.
- Follow sick-day, contrast, and fasting instructions exactly.
Tip: Let your CGM or meter be your coach—test before and 60–120 minutes after coffee to see your personal response.
Disclaimer: Informational only; not medical advice. Your clinician’s guidance for your condition takes priority.
In conclusion, harnessing the power of coffee with metformin can be a valuable strategy for individuals looking to enhance their weight loss results. By leveraging the metabolic benefits of both substances, individuals may experience improved appetite control, increased fat burning, and enhanced calorie expenditure. However, it is essential to approach this strategy with caution and under medical supervision. Coffee with metformin should be integrated into a comprehensive lifestyle approach that includes a healthy diet and regular physical activity for sustainable weight loss success.






