OneHundredCoffee is reader-supported, and some products displayed may earn us an affiliate commission. Details
Can You Drink Coffee While Taking Antiandrogens?
Antiandrogens do one big job: they turn down testosterone’s “volume” so the rest of your care plan can work with fewer distractions. Whether it’s bicalutamide or flutamide as a first step, or next-gen agents like enzalutamide, apalutamide, darolutamide, or older nilutamide, the goal is the same—steady symptom control with side effects kept as quiet as possible. Coffee is your daily ritual on the other side of that equation: familiar, comforting, and (for many of us) part of how mornings make sense. You don’t have to pick one over the other. With a few small tweaks, you can keep the cup you love while your medication keeps doing its work.
Start with how the combo feels in your body. A fast, very hot, acidic mug on an empty stomach is the most likely to spark reflux, racing heart, or a jittery edge—especially if the medicine already leans sedating or makes you a little light-headed when you stand. Two smaller, smoother cups across the morning almost always land better than one giant slug. Paper-filtered drip or pour-over tends to feel gentler than unfiltered methods; on days when sleep or stomach is touchy, a diluted cold brew or a low-acid decaf is the softest path.
Timing is your quiet superpower. Give your dose its own moment, then enjoy coffee with or after food. If you’re especially sensitive to caffeine, try a modest 45–60 minute buffer. Protect sleep, too—late-day caffeine stretches bedtime and can make hot flashes, reflux, or nighttime restlessness feel louder. Parking your last fully caffeinated cup in the early afternoon, then keeping the evening ritual with a smooth decaf, is a simple, high-yield tweak.
Hydration fixes more than you’d think. Match each cup with water. If you stand up and feel woozy, that’s your cue to shrink the serving, slow the sip, add fluids, and anchor coffee to a snack or meal. Finally, personalize for a week: watch four signals—energy, reflux, sleep, and how you feel 20–30 minutes after dosing. Keep what works; adjust what doesn’t. The whole point is a calm, repeatable routine where your antiandrogen keeps working and your coffee still tastes like you.
Below is an at-a-glance table for common antiandrogens with Practical guidance, Simple timing tips, and a gentle “Safest beans pick.”
Coffee × Antiandrogens — Quick Guide & Safest Beans Picks
| Medicine | Coffee effect snapshot | Practical guidance | Simple timing tip | Safest beans pick* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enzalutamide | May feel activating; big fast mugs can add restlessness or reflux. | Favor paper-filtered drip; keep portions modest; match each cup with water. | Place coffee with/after breakfast; keep last caffeinated cup early afternoon. | Lavazza Dek Decaf — Whole Bean, 1.1 lb |
| Apalutamide | Steady routines pair best; very hot/acidic cups may aggravate heartburn. | Choose low-acid decaf or half-caff; sip slowly; keep add-ins simple. | Coffee 30–60 min after a light meal. | Peet’s Decaf Major Dickason’s — Whole Bean, 12 oz |
| Darolutamide | Usually friendly with small/medium coffee; late caffeine can disturb sleep. | Keep servings modest; consider decaf/half-caff on “edgy” days. | Anchor the last caffeinated cup in early afternoon. | Coffee Bros Colombian Decaf — Whole Bean, 12 oz |
| Bicalutamide | Large, fast mugs can feel jittery yet still impair sleep. | Gentle medium roasts or decaf; hydrate; pair coffee with food. | Enjoy coffee with/after breakfast; avoid late-evening caffeine. | Caribou Coffee Decaf Blend — K-Cup Pods, 24 ct |
| Flutamide | Acidic coffee may poke reflux; oversized mugs can add palpitations. | Prefer low-acid decaf or diluted cold brew; keep portions small. | If sensitive, leave ~45–60 min between dose and coffee. | Kicking Horse Decaf (Swiss Water) — Whole Bean, 10 oz |
| Nilutamide | Moderate coffee often fine; keep routine predictable during adjustment. | Small, smooth cups; add a glass of water alongside. | Place coffee after a light meal; avoid chugging on empty stomach. | Equal Exchange Organic Decaf — Whole Bean, 12 oz |
*“Safest beans” = typically low-acid, decaf, or half-caff options that many readers find gentler on reflux, sleep, and day-to-day steadiness. Personalize to your own tolerance and clinician advice.
In conclusion, antiandrogens play a vital role in managing conditions related to excessive androgen activity in the body. By understanding their mechanism of action—whether through receptor blocking, enzyme inhibition, or GnRH agonism—we can appreciate how these medications suppress testosterone and mitigate its unwanted effects.
The Rise Of Coffee With Antiandrogens: A New Trend In Hormone Regulation
In recent years, a new trend has emerged in the realm of hormone regulation – the rise of coffee with antiandrogens. As individuals become more conscious about their hormonal balance and seek natural ways to manage it, this unique blend has gained popularity for its potential health benefits. This article explores the growing trend of coffee with antiandrogens and delves into its potential implications for hormone regulation.
Antiandrogens are substances that inhibit or block the effects of androgens, which are male sex hormones like testosterone. While primarily used for medical purposes such as treating conditions like prostate cancer or excessive hair growth, some individuals have started incorporating them into their daily routine by adding them to their morning cup of coffee.
The concept behind coffee with antiandrogens is simple yet intriguing. By combining a natural substance known to affect hormone levels with one of the most widely consumed beverages worldwide, proponents believe they can harness additional benefits for hormone regulation.
One commonly used antiandrogen in this context is spearmint tea. Studies have shown that spearmint tea possesses antiandrogenic properties and may help reduce testosterone levels in women suffering from polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). When added to coffee, it not only enhances the flavor but also provides an additional avenue for reaping these potential health benefits.
Another popular choice is saw palmetto extract, derived from the berries of a small palm tree native to North America. Saw palmetto has been traditionally used as an herbal remedy for various conditions, including benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), which involves an enlargement of the prostate gland caused by increased androgen activity. By incorporating saw palmetto extract into their daily cup of joe, enthusiasts hope to regulate their hormonal balance naturally while enjoying their morning ritual.
While scientific research on the direct effects of these substances when combined with coffee is limited, anecdotal evidence suggests that coffee with antiandrogens may have positive effects on hormone regulation. Many individuals claim to experience improvements in symptoms related to hormonal imbalances, such as reduced acne breakouts or improved mood stability.
However, it is important to note that the effects of coffee with antiandrogens may vary depending on individual factors and the specific hormonal imbalances one seeks to address. Consulting a healthcare professional before incorporating any new substance into your routine is always recommended.
In conclusion, the rise of coffee with antiandrogens represents a new trend in hormone regulation. By blending natural substances known for their potential antiandrogenic properties with the beloved morning beverage, individuals hope to achieve improved hormonal balance. While further research is needed to fully understand its effectiveness and potential side effects, this unique combination continues to gain popularity as people seek alternative ways to manage their hormones naturally.
How Coffee Can Potentially Enhance The Effects Of Antiandrogens
Coffee, one of the most popular beverages worldwide, has long been recognized for its stimulating effects on the central nervous system. However, recent research suggests that coffee may have additional benefits when consumed alongside antiandrogen medications. Antiandrogens are a class of drugs commonly prescribed to treat conditions such as prostate cancer, hirsutism, and hormonal acne. Understanding how coffee can potentially enhance the effects of antiandrogens is crucial for optimizing their therapeutic outcomes.
Firstly, coffee contains various bioactive compounds that have been found to exhibit antiandrogenic properties. One such compound is caffeine, a central nervous system stimulant and adenosine receptor antagonist. Caffeine has been shown to inhibit testosterone synthesis in Leydig cells within the testes, reducing circulating androgen levels in both animals and humans. By lowering testosterone levels through this mechanism, caffeine may work synergistically with antiandrogens to further suppress androgen activity.
Moreover, coffee is rich in phytochemicals like flavonoids and polyphenols that possess antioxidant properties. These compounds have demonstrated anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting inflammatory mediators such as nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) signaling pathways. Chronic inflammation plays a pivotal role in the development and progression of various diseases related to excess androgen activity, including acne vulgaris. By reducing inflammation through its antioxidant components, coffee consumption may complement the action of antiandrogens in managing these conditions.
Furthermore, studies have indicated that certain constituents present in coffee might modulate sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) levels—a protein responsible for binding sex hormones like testosterone and estradiol—thus influencing their availability within the body. Some research suggests that coffee intake increases SHBG concentrations, consequently resulting in decreased free testosterone levels. As free testosterone is more biologically active than bound testosterone or other sex hormones, the reduction of its levels may enhance the efficacy of antiandrogen medications.
Additionally, coffee has been associated with improved insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism. Insulin resistance is a common feature in conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), which is often accompanied by excessive androgen production. By enhancing insulin sensitivity, coffee consumption may indirectly modulate androgen levels, potentially synergizing with antiandrogens in managing PCOS-related symptoms. Although these findings suggest the potential benefits of coffee in enhancing the effects of antiandrogens, it is important to note that individual responses may vary due to factors such as genetics, metabolism, and overall health status.
Moreover, excessive coffee consumption can have adverse effects on cardiovascular health or disrupt sleep patterns. Therefore, before incorporating coffee into an antiandrogen regimen, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional to determine an appropriate dosage and ensure compatibility with other medications or underlying conditions.
Brewing Methods For Optimal Extraction Of Antiandrogenic Compounds In Coffee
Coffee is not only a popular beverage worldwide but also a potential source of antiandrogenic compounds, which have been linked to several health benefits. To fully harness these compounds, it is essential to understand the brewing methods that maximize their extraction. This subtopic explores various brewing techniques that can enhance the concentration of antiandrogens in your cup of coffee.
The water temperature plays a crucial role in extracting antiandrogenic compounds from coffee beans. Using water at an optimal temperature between 195°F (90°C) and 205°F (96°C) ensures efficient extraction while preventing excessive bitterness or acidity. Experiment with different temperatures within this range to find the sweet spot for your taste preferences.
The size of coffee grounds impacts the surface area exposed during brewing, affecting extraction rates. For optimal extraction of antiandrogenic compounds, aim for a medium grind size that resembles granulated sugar. Avoid very fine grinds as they may result in over-extraction and bitterness, whereas larger grinds may under-extract desired compounds.
The duration of brewing directly influences the amount of antiandrogens extracted from coffee beans into your cup. Generally, a brew time between four to six minutes allows sufficient contact between water and coffee grounds for optimal extraction without compromising flavor or balance.
Different brewing methods offer unique opportunities to extract antiandrogens effectively:
– Pour Over: This method involves pouring hot water over coffee grounds placed in a filter cone or dripper. Its slow and controlled pouring technique allows for precise control over the water flow rate, ensuring thorough extraction.
– French Press: In this method, ground coffee is steeped in hot water before being separated by pressing down on a plunger with a mesh filter. The extended contact time between water and coffee grounds promotes effective extraction.
– Espresso: The espresso brewing process involves forcing hot water through finely ground coffee under high pressure. Although the brew time is significantly shorter, the pressurized extraction enhances the concentration of antiandrogenic compounds.
– Cold Brew: Cold brewing relies on steeping coffee grounds in cold or room temperature water for an extended period, typically 12 to 24 hours. This method tends to produce a smoother and less acidic cup while extracting antiandrogens more slowly.
Remember that experimenting with these brewing methods is key to finding your preferred balance of flavor and enhanced extraction of antiandrogenic compounds. Adjusting variables such as grind size, brew time, and water temperature allows you to personalize your coffee experience while maximizing its potential health benefits.
Coffee and Enzalutamide
Coffee With Enzalutamide: A Promising Combination for Prostate Cancer Treatment
In recent years, enzalutamide has emerged as a revolutionary antiandrogen medication in the treatment of prostate cancer. This powerful drug has demonstrated remarkable efficacy in blocking androgen receptors, effectively suppressing the growth and spread of prostate cancer cells. However, like any medication, enzalutamide comes with its own set of challenges and side effects. Could combining this medication with our beloved morning brew provide a solution?
Enzalutamide is renowned for its ability to inhibit the binding of androgens to their receptors, thereby preventing them from fueling tumor growth. This targeted approach has shown tremendous promise in slowing down disease progression and extending survival rates for men with advanced prostate cancer. However, the use of enzalutamide often leads to fatigue, cognitive impairment, hot flashes, and other side effects that can significantly impact patients’ quality of life.
This is where coffee comes into play as a potential ally in mitigating these adverse effects. Coffee is widely consumed worldwide and known for its stimulating properties due to its caffeine content. Caffeine acts as a central nervous system stimulant, boosting alertness and reducing fatigue. By incorporating coffee into the routine of patients taking enzalutamide, it may be possible to counteract some of the fatigue associated with this antiandrogen therapy.
Moreover, research suggests that coffee might have additional benefits beyond combating fatigue. Several studies have linked regular coffee consumption to a reduced risk of developing certain types of cancer – including prostate cancer – potentially complementing the action of enzalutamide in battling tumor growth. Additionally, coffee contains antioxidant compounds that exhibit anti-inflammatory properties; this could help alleviate some symptoms caused by inflammation triggered by enzalutamide treatment.
However promising these findings may be, caution must be exercised when considering coffee as an adjuvant therapy alongside enzalutamide. It is essential to consult with healthcare professionals to ensure that coffee consumption does not interfere with the absorption or metabolism of enzalutamide or interact negatively with any other medications a patient may be taking.
In conclusion, combining coffee with enzalutamide in prostate cancer treatment holds significant potential for improving patients’ well-being and enhancing the effectiveness of therapy. The stimulant properties of coffee could counteract fatigue, while its potential anti-inflammatory effects and cancer-fighting properties may provide additional benefits. Nevertheless, it is crucial to approach this combination cautiously and seek medical advice before making any changes to medication or dietary routines.
Coffee and Apalutamide
Coffee with Apalutamide: Exploring the Intersection of Antiandrogens and Prostate Cancer Treatment
As medical advancements continue to shape the landscape of cancer treatment, researchers are constantly striving to develop innovative therapies. One such breakthrough in prostate cancer management is the use of antiandrogens, a class of drugs that inhibit the action or production of male sex hormones. Among these drugs, apalutamide has emerged as a promising option for patients battling this common form of cancer.
In this article, we delve into the details surrounding apalutamide and its potential impact on prostate cancer treatment.
Apalutamide belongs to a group of medications known as nonsteroidal antiandrogens. It works by blocking the interaction between androgen receptors and testosterone, effectively suppressing the growth and progression of prostate cancer cells. Approved by regulatory authorities for use in advanced prostate cancer cases, apalutamide offers new hope to patients who have exhausted other treatment options.
When considering apalutamide therapy, it is crucial to understand its potential side effects. While generally well-tolerated, some patients may experience adverse reactions such as fatigue, rash, falls/fractures, or hypertension. However, with proper medical supervision and monitoring, these side effects can be managed effectively.
Another important aspect associated with apalutamide is its role in delaying disease progression in non-metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (nmCRPC). This condition refers to cases where prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels continue to rise despite hormone therapy and no visible signs of metastasis are present. Studies have shown that apalutamide significantly prolongs metastasis-free survival among nmCRPC patients compared to placebo treatments.
Additionally, combining apalutamide with other standard therapies has demonstrated significant benefits in treating advanced forms of prostate cancer. In clinical trials evaluating its efficacy when used alongside hormonal therapy or following surgical removal of the prostate gland (radical prostatectomy), apalutamide has shown impressive results in reducing the risk of disease recurrence or metastasis.
Coffee with apalutamide would not be complete without discussing ongoing research and future directions. Scientists are actively investigating its potential use in earlier stages of prostate cancer, as well as in combination with immunotherapy or radiation therapy. The aim is to optimize treatment outcomes by tailoring therapies according to individual patient characteristics and disease stages.
In conclusion, apalutamide represents a significant advancement in the treatment of prostate cancer. By inhibiting androgen receptors, this antiandrogen drug offers new hope for patients battling advanced forms of the disease. With ongoing research and clinical trials exploring its potential applications, the future seems bright for coffee with apalutamide as part of a comprehensive approach to managing prostate cancer effectively.
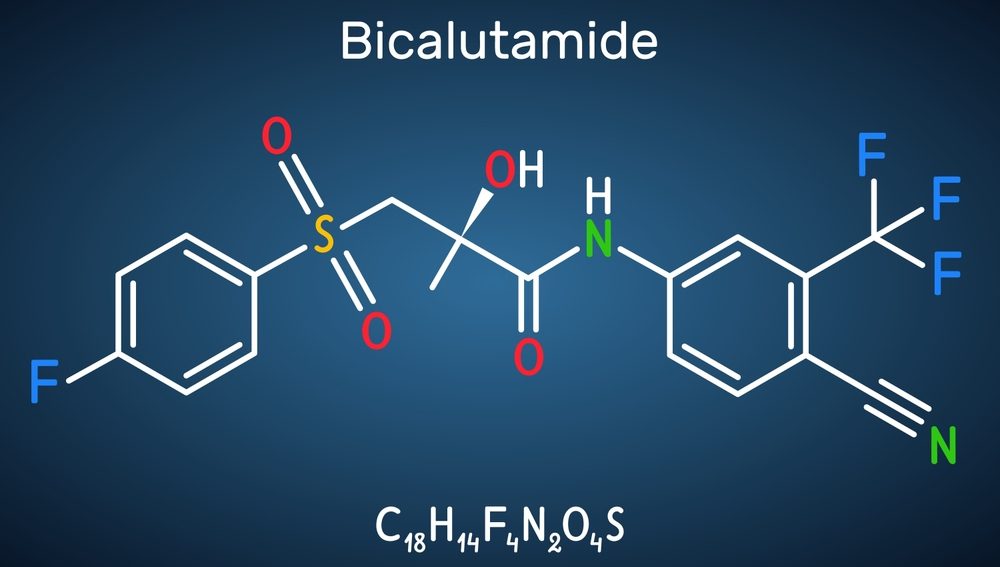
Coffee and Bicalutamide
Coffee With Bicalutamide: The Potential Benefits and Considerations
In recent years, coffee has become a staple beverage for many individuals around the world. Its rich aroma, bold flavor, and energy-boosting properties have made it a favorite morning ritual for millions. However, what if we told you that coffee could potentially have an unexpected companion in the form of antiandrogens? One such antiandrogen is bicalutamide – a medication primarily used to treat prostate cancer.
While combining coffee with bicalutamide may seem like an unusual pairing, there are several potential benefits and considerations to explore.
Bicalutamide belongs to a class of medications known as antiandrogens, which work by blocking the effects of androgens (male sex hormones) in the body. By inhibiting these hormones, bicalutamide can help slow down or stop the growth of prostate cancer cells. Interestingly, recent studies have suggested that certain compounds found in coffee may also possess anti-cancer properties. These compounds include caffeine, chlorogenic acid, and cafestol – all of which have been associated with potentially protective effects against various types of cancers.
One possible benefit of combining coffee with bicalutamide lies in its potential to combat prostate cancer. While research is still ongoing regarding this specific combination therapy, preliminary studies suggest that coffee consumption might enhance the effectiveness of certain anticancer drugs by increasing their absorption or reducing drug resistance mechanisms within cancer cells. Therefore, consuming coffee alongside bicalutamide treatment could potentially lead to improved outcomes for individuals battling prostate cancer.
However, it is essential to approach this combination therapy with caution and consider some important factors before incorporating it into your routine. Firstly, it’s crucial to consult with your healthcare provider before making any changes to your treatment plan or adding new substances such as coffee to your regimen. They can provide personalized advice based on your medical history and current condition.
Moreover, it’s important to be mindful of coffee’s potential side effects and interactions with medications. Coffee is a natural stimulant that can increase heart rate and blood pressure, and cause sleep disturbances. Therefore, individuals with cardiovascular issues or insomnia may need to exercise caution when combining coffee with bicalutamide or any other medication.
In conclusion, the idea of enjoying a cup of coffee alongside bicalutamide treatment for prostate cancer may hold promise due to the potential synergistic effects between coffee compounds and antiandrogens. However, it is crucial to remember that research in this area is still evolving, and individual variations may exist regarding the impact of this combination therapy. Always consult with your healthcare provider before making any changes to your treatment plan and consider any potential risks or interactions that could arise from adding coffee to your routine.
Coffee and Darolutamide
Coffee with Darolutamide: A Promising Antiandrogen in the Fight Against Prostate Cancer
In recent years, the field of prostate cancer treatment has witnessed significant advancements with the development of novel targeted therapies. Among these breakthroughs, darolutamide has emerged as a promising antiandrogen that holds great potential in combating this prevalent disease. This article aims to delve into the world of darolutamide and explore its mechanism of action, efficacy, safety profile, and prospects.
Darolutamide belongs to a class of drugs called nonsteroidal antiandrogens (NSAA) and works by inhibiting the binding of androgens to their receptors. By blocking this interaction, darolutamide effectively suppresses the growth signaling pathways that promote prostate cancer cell proliferation. Unlike other antiandrogens, darolutamide exhibits a high affinity for the androgen receptor while displaying minimal off-target effects on other hormone receptors. This selectivity contributes to its enhanced therapeutic efficacy and improved tolerability.
Clinical trials have demonstrated compelling evidence regarding darolutamide’s efficacy in treating prostate cancer. The ARAMIS trial, one of the pivotal studies evaluating darolutamide’s effectiveness in patients with non-metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (nmCRPC), revealed remarkable results. Patients receiving darolutamide experienced a significantly prolonged metastasis-free survival compared to those on placebo. Furthermore, this benefit was observed without compromising overall survival or quality of life.
Moreover, what sets darolutamide apart is its favorable safety profile. Common side effects include fatigue and hypertension; however, these adverse events are generally manageable with supportive care measures or dose adjustments if necessary. Unlike some other antiandrogens that can cause central nervous system-related side effects like cognitive impairment or seizures, darolutamide has not shown any significant impact on cognitive function.
The future outlook for coffee with darolutamide seems promising as well. Ongoing clinical trials are investigating its potential in various stages of prostate cancer, including metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer. Early data suggest that darolutamide, when combined with standard androgen deprivation therapy, may enhance treatment outcomes in this patient population.
In conclusion, darolutamide offers a ray of hope for men battling prostate cancer. As an effective antiandrogen with a favorable safety profile, it has the potential to revolutionize the management of this disease. By inhibiting androgen receptor signaling pathways and consequently suppressing tumor growth, darolutamide provides patients with an extended period free from metastasis without compromising their overall quality of life.
Coffee and Nilutamide
Coffee With Nilutamide: A Promising Combination for Hormone Therapy
Nilutamide, a powerful antiandrogen medication, has gained recognition for its effectiveness in treating certain hormone-related conditions. When combined with coffee, this drug may offer even more benefits and potential synergistic effects. In this subtopic, we will explore the potential advantages of “coffee with nilutamide” as a unique approach to hormone therapy. Nilutamide is primarily used in the treatment of prostate cancer, specifically those that are hormone-sensitive.
As an antiandrogen, it works by blocking the actions of male hormones, such as testosterone, which can fuel the growth of prostate cancer cells. By inhibiting these hormones’ activity, nilutamide helps slow down tumor growth and reduces symptoms associated with advanced prostate cancer. When consumed alongside coffee, nilutamide’s efficacy may be further enhanced due to several factors. Firstly, coffee contains various bioactive compounds like polyphenols and caffeine that have been linked to potential health benefits.
These compounds possess antioxidant properties and exhibit anti-inflammatory effects that could complement nilutamide’s action against cancer cells. Moreover, research suggests that coffee consumption may play a role in modulating hormone levels in the body. Studies have shown that coffee intake can affect sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG), a protein responsible for binding sex hormones like testosterone and estrogen. By increasing SHBG levels, coffee may help reduce circulating levels of testosterone—effectively supporting the antiandrogenic effects of nilutamide.
Coffee also acts as a natural adjuvant to drug therapy due to its ability to enhance drug absorption and metabolism. Certain substances found in coffee can influence enzymes responsible for drug metabolism in the liver (e.g., cytochrome P450 enzymes). This interaction can potentially impact how drugs are processed within the body and thus affect their therapeutic efficacy. In addition to these pharmacological interactions between nilutamide and coffee compounds themselves, the ritualistic and psychological aspects of enjoying a cup of coffee can also contribute to improved patient outcomes.
The simple act of having coffee can enhance mood, reduce stress, and improve overall quality of life—factors that are crucial for patients undergoing hormone therapy. It is important to note that while coffee consumption may have potential benefits when combined with nilutamide, individual responses may vary. Patients should consult with their healthcare providers before incorporating this combination into their treatment plan.
Additionally, more research is needed to fully understand the specific mechanisms and optimal dosages for achieving maximal therapeutic effects.
In conclusion, combining nilutamide with coffee presents a unique approach to hormone therapy for prostate cancer patients. The potential synergistic effects between nilutamide’s antiandrogenic properties and coffee’s bioactive compounds make this combination worth exploring further.
Coffee and Flutamide
Coffee with Flutamide: A Promising Combination for Hormone Balancing
In recent years, there has been growing interest in the potential benefits of combining certain medications with natural substances to enhance their therapeutic effects. One such combination that has gained attention is “coffee with flutamide.” Flutamide, an antiandrogen medication primarily used to treat prostate cancer and hirsutism, has shown promising results when paired with coffee in addressing hormone imbalances.
Flutamide works by blocking the effects of androgens, male hormones responsible for various physiological processes. Inhibiting androgen receptors helps regulate the production and activity of these hormones. However, as with any medication, flutamide may come with certain side effects or limitations. This is where coffee comes into play as a potential complementary component.
Coffee contains numerous bioactive compounds that have been linked to various health benefits. Caffeine is perhaps the most well-known component of coffee and has been associated with increased alertness and cognitive function. However, it also exhibits properties that can potentially aid in hormone regulation.
Research suggests that caffeine may influence sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) levels in the body. SHBG is a protein that binds to sex hormones like testosterone and estrogen, rendering them inactive. By increasing SHBG levels, caffeine could potentially help balance hormone levels by reducing the availability of free active hormones.
When combined with flutamide’s antiandrogenic properties, coffee’s potential hormonal balancing effects become even more intriguing. Coffee could enhance flutamide’s ability to inhibit androgens while concurrently supporting overall hormonal equilibrium through its impact on SHBG levels.
Moreover, studies have indicated that coffee consumption may lower insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) levels in the body, an important factor in regulating cell growth and proliferation. Elevated IGF-1 levels have been associated with increased risk for certain cancers and other health conditions. By potentially reducing IGF-1 levels, coffee could further contribute to the overall benefits of flutamide therapy.
Although the combination of coffee and flutamide shows promise in hormone regulation, it is important to consult with healthcare professionals before incorporating this combination into your routine. They can provide personalized guidance based on your specific health needs and potential interactions with other medications or conditions.
In conclusion, “coffee with flutamide” presents a fascinating approach to addressing hormone imbalances. By combining the antiandrogenic effects of flutamide with the potential hormone-balancing properties of coffee, this novel combination could offer new avenues for managing conditions related to hormonal dysregulation. However, further research is needed to better understand the mechanisms underlying this interaction and its full therapeutic potential.
Conclusion And Future Directions: Is ‘Coffee With Antiandrogens’ Worth Exploring Further?
In conclusion, the emerging evidence on the potential antiandrogenic effects of coffee consumption suggests that further exploration of this intriguing topic is warranted. Although the literature is still limited, the existing studies provide valuable insights into the complex interaction between coffee and androgen hormones.
Firstly, several epidemiological studies have consistently shown an inverse association between coffee intake and serum testosterone levels in men. These findings are supported by experimental research demonstrating the ability of certain coffee compounds to inhibit testosterone production or disrupt androgen receptor signaling pathways. Such evidence highlights the potential of coffee as a natural source of antiandrogens.
Moreover, the antiandrogenic properties of coffee may have important implications for various health conditions related to androgen excess or dysregulation. For instance, hyperandrogenism is a common feature in disorders like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or hirsutism. If coffee truly possesses antiandrogenic effects, it could be explored as a dietary intervention to alleviate symptoms associated with these conditions.
Furthermore, considering that excessive androgens play a role in the development and progression of certain cancers, such as prostate cancer, understanding how coffee modulates androgens could have therapeutic implications. Identifying specific compounds responsible for these effects would allow for targeted interventions or even drug development based on natural sources.
However, it is important to acknowledge several limitations within the current body of research on this topic. Firstly, most studies conducted so far are observational, which limits our ability to establish causality definitively. Additionally, variations in study design and methods make it challenging to draw consistent conclusions across different investigations.
Therefore, future research should aim to address these limitations by conducting well-designed randomized controlled trials that include diverse populations. Longitudinal studies examining changes in hormone levels following regular coffee consumption would also provide valuable insights into potential mechanisms of action. Furthermore, investigating the impact of different coffee brewing methods, roasting levels, and types of coffee beans on antiandrogenic effects could help identify optimal conditions for obtaining these benefits.
Caffeine and Antiandrogens: What Every Patient Should Know — FAQ
Covers common antiandrogens and androgen-suppressing therapies (e.g., spironolactone, finasteride, dutasteride, bicalutamide, GnRH analogs, androgen deprivation in prostate cancer). Educational only—always follow your own prescriber’s advice.
1) Does caffeine interfere with how antiandrogens work?
For most commonly used antiandrogens and androgen-lowering regimens, usual dietary caffeine does not “switch off” the drug. Their effect comes from hormone pathways and receptors that coffee does not directly block.
2) Which medications are we talking about?
This FAQ speaks generally to spironolactone, finasteride, dutasteride, bicalutamide, flutamide, enzalutamide, abiraterone (with steroids), GnRH analogs, and similar agents used for androgen suppression, prostate cancer, androgenetic alopecia, acne, or gender-affirming care.
3) Can caffeine change my hormone levels or testosterone?
Studies show mixed, often small effects. Typical caffeine doses may cause minor, temporary shifts, but not enough to override prescribed antiandrogen therapy. Your medication is the main driver of androgen suppression.
4) Is it safe to drink coffee on spironolactone?
Usually yes, in moderation. The key with spironolactone is monitoring potassium, kidney function, and blood pressure. Heavy caffeine plus a diuretic effect may increase urination; ensure you are drinking enough non-caffeinated fluids.
5) What about finasteride or dutasteride and caffeine?
No meaningful interaction is expected. These drugs block conversion of testosterone to DHT; caffeine at usual doses does not counteract that mechanism. Keep coffee moderate and consistent with your normal routine.
6) Can caffeine worsen side effects of antiandrogens?
It can overlap with some symptoms: fatigue masked by caffeine, anxiety, palpitations, or sleep disruption. If you already feel emotionally or physically fragile on therapy, high caffeine might make that feel harsher—dial down if needed.
7) I’m on androgen deprivation for prostate cancer—can I keep my morning coffee?
In most cases, yes. Focus on overall heart health, bone health, hydration, sleep, and weight management. One to two cups of coffee is commonly acceptable; confirm limits with your oncology team, especially if you have heart rhythm issues.
8) Does coffee timing around my dose matter?
For most antiandrogens there is no strict coffee–dose rule. A simple approach: keep your medication time consistent, and enjoy coffee in a stable daily pattern so your body is not constantly dealing with big caffeine swings.
9) How much caffeine per day is reasonable on these therapies?
Many adults do well at up to about 200–300 mg/day while on hormone-modifying therapy, but some need less. If you have hypertension, arrhythmias, anxiety, or sleep issues, aim lower or include decaf.
10) Is decaf a safer or smarter option?
Often yes. Decaf keeps the ritual and flavor with minimal influence on heart rate, sleep, or jitters—useful when your body is already adapting to hormonal changes.
11) Do energy drinks or high-dose caffeine pills pose extra risk?
Yes, they can. Very high caffeine doses may stress the heart, disturb sleep, and worsen anxiety. This is especially concerning if your therapy already affects cardiovascular risk. Stick to gentler sources like coffee or tea in moderate amounts.
12) Could caffeine affect my mood or dysphoria while on antiandrogens?
Caffeine can amplify anxiety, restlessness, or irritability in some people. If your mood feels unstable, experiment with reducing caffeine and see whether your emotional baseline becomes smoother.
13) Any food or drink I must avoid completely with these meds?
This depends on the specific drug: some have interactions with certain acids, alcohol, or liver enzyme modulators. Coffee itself is not usually on the “forbidden” list, but always read your exact medication guide.
14) Can caffeine change drug levels through the liver (CYP) system?
Caffeine is metabolized by liver enzymes too, but at usual intake it is not a strong enough influencer to be the main concern for most antiandrogens. Other prescription drugs and supplements are more relevant here than coffee.
15) I feel very tired on treatment—should I just push more caffeine?
It’s tempting, but not ideal. Fatigue may be from hormonal shifts, anemia, mood changes, poor sleep, or the underlying condition. Masking it with heavy caffeine can backfire. Discuss persistent fatigue with your clinician instead of escalating doses on your own.
16) Any concerns about blood pressure or heart rhythm?
Some antiandrogen regimens and related therapies can influence cardiovascular risk. If you have a history of arrhythmia, hypertension, or heart disease, keep caffeine modest and consistent and monitor how you feel.
17) What about bone health and caffeine while on long-term androgen suppression?
Long-term androgen suppression can affect bone density. High caffeine plus low calcium/vitamin D, smoking, or inactivity may add up. Use caffeine in moderation and follow bone-health strategies from your team.
18) Does coffee affect hair-loss treatment results (finasteride/dutasteride)?
No strong evidence that normal caffeine intake reverses the benefits of these medications. Consistency with your pill is far more important than small variations in daily coffee.
19) When should I reduce or stop caffeine completely?
Consider cutting back if you have severe anxiety, insomnia, strong palpitations, uncontrolled blood pressure, or your clinician advises stricter limits for heart or other conditions.
20) Key practical rules to keep coffee and antiandrogens compatible?
- Take your medication exactly as prescribed; do not change doses based on caffeine.
- Use moderate, steady caffeine; favor decaf if symptoms flare.
- Protect sleep; avoid large late-evening doses.
- Watch mood, heart rate, and blood pressure; adjust if you notice patterns.
- Discuss any big diet or supplement changes with your clinician.
Tip: Treat coffee as a comfort ritual, not a hormone controller. Your prescription does the therapeutic work.
Disclaimer: This FAQ is for education only and does not replace individualized medical advice. Always confirm with your treating clinician.
In conclusion, while “Coffee with Antiandrogens” is a relatively new and evolving area of research, the available evidence suggests that exploring this topic further is justified. The potential health implications related to androgen regulation and the natural availability of coffee make it an attractive avenue for investigation. By addressing existing limitations and conducting rigorous studies, we can gain a deeper understanding of the antiandrogenic properties of coffee and potentially harness its benefits for various health conditions.






